
Telemetry Technician Course EKG Lead Placement (class 3)
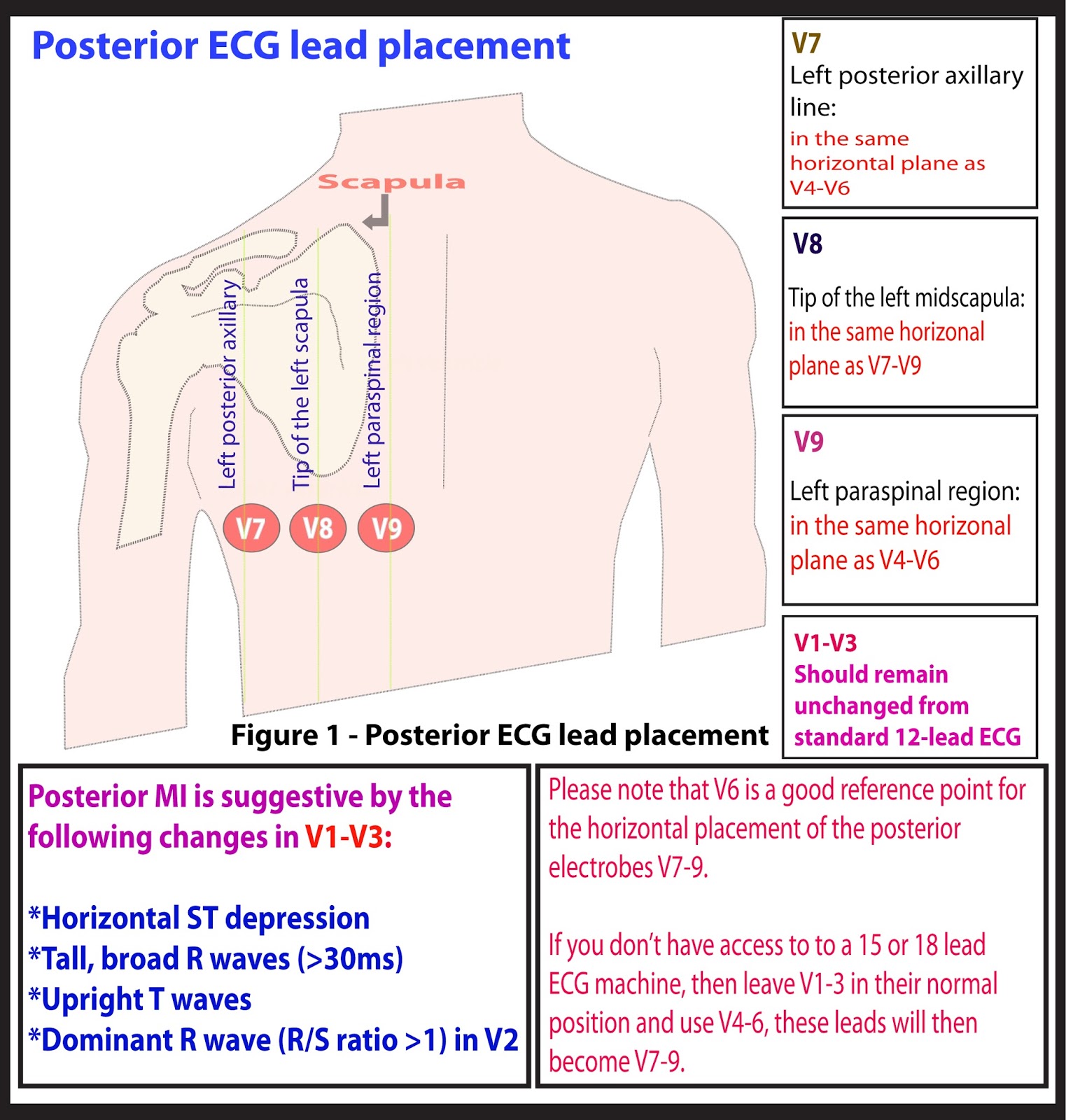
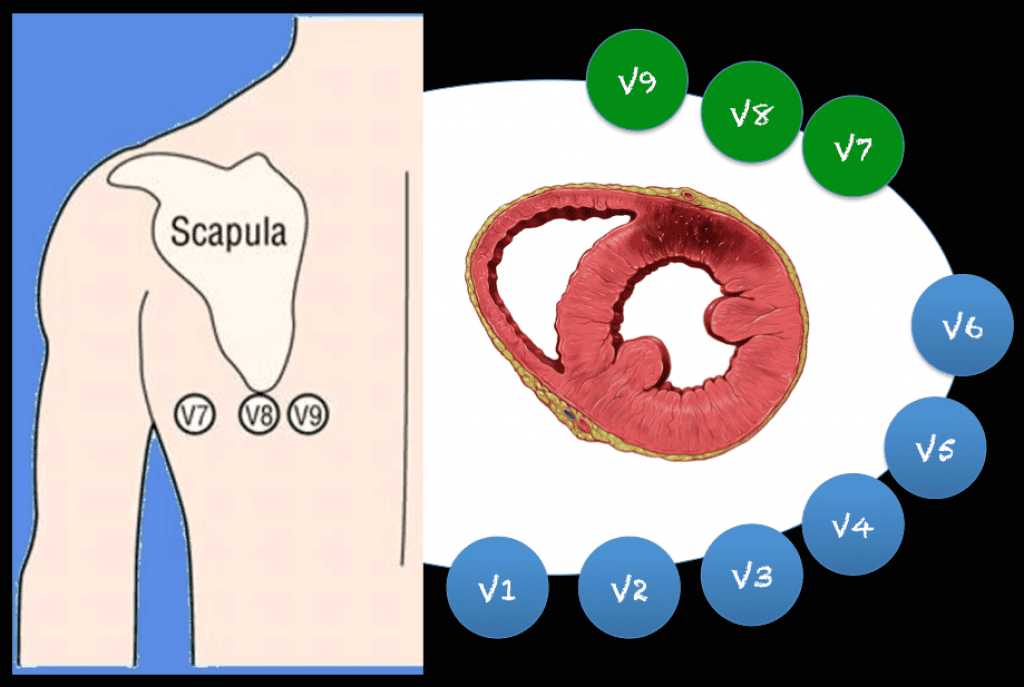
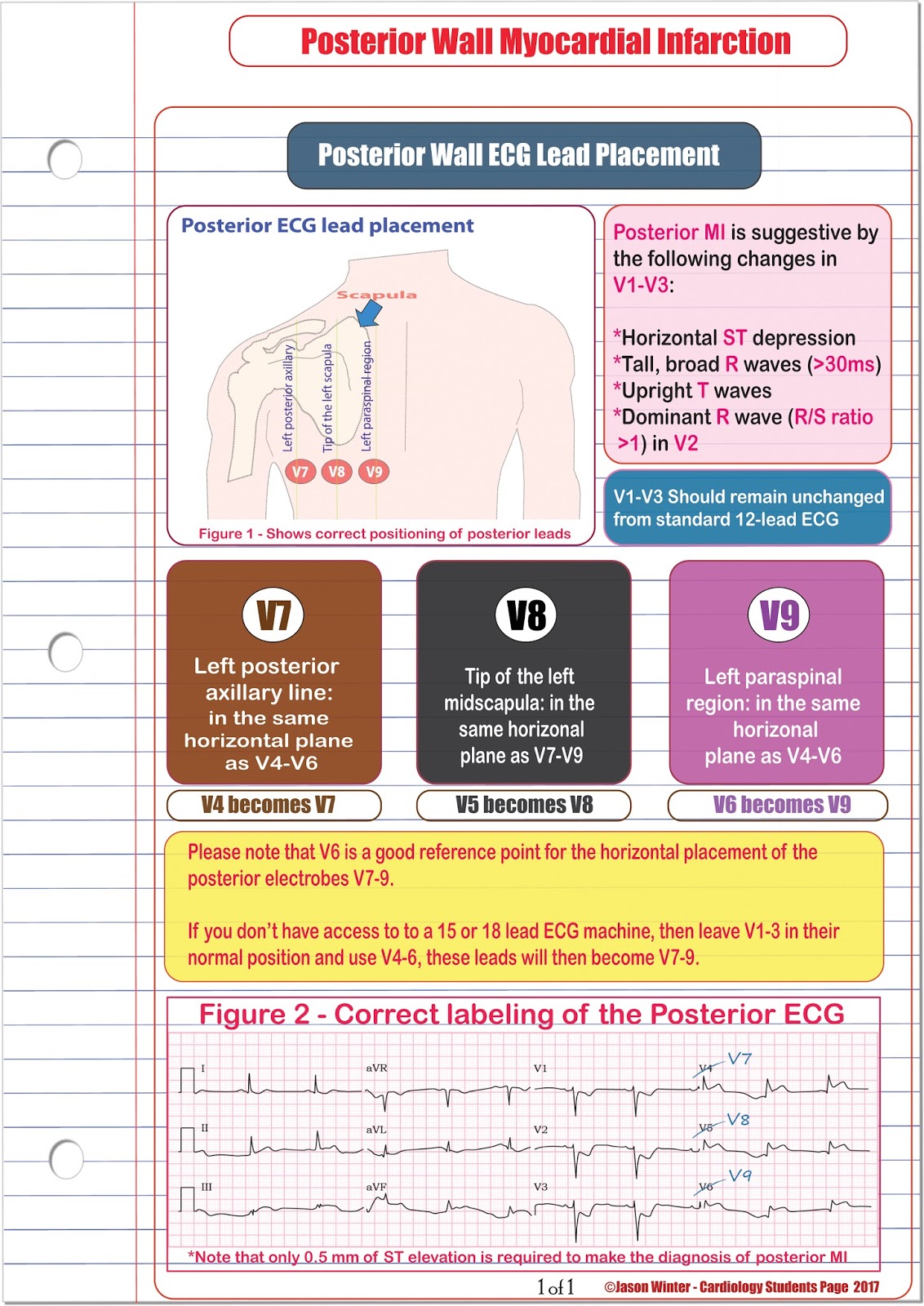
The addition of posterior leads V 7 to V 9 significantly increases the ability to detect posterior injury patterns compared with the standard 12-lead ECG. 5, 7 Lead V 7 should be placed at the level of lead V 6 at the posterior axillary line, lead V 8 on the left side of the back at the tip of the scapula, and lead V 9 halfway between lead V 8 and the left paraspinal muscles.
ECG Educator Blog Posterior ECG Lead Placement
The leads V4-V6 are removed and substituted for V7-V9 as shown below. On most EKg machines, the labels areno automatically changed so it is important to cross out the labels for V4-V6 and write in V7-V9. It is also helpful for future clinicians, if you note in your read that it is a posterior ECG.

Pin on Nursing Cardiac
5-electrode system Uses 5 electrodes (RA, RL, LA, LL and Chest) Monitor displays the bipolar leads (I, II and III) AND a single unipolar lead (depending on position of the brown chest lead (positions V1-6)) 5-lead electrode placement 12-lead ECG 10 electrodes required to produce 12-lead ECG
Proper Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) Lead Placement ECGEDU
To detect posterior STEMI associated with occlusion of the circumflex artery or dominant right coronary artery, obtain a posterior ECG. 2-3 [Level A Recommendation] When a 15-lead &/or 18-lead ECG machine is not available, manipulation of the leads from a standard 12-lead ECG machine allow additional areas of the heart to be imaged.4-5

ECG Educator Blog Posterior ECG Lead Placement
An American Heart Association Scientific statement reports that recordings from right-sided and posterior ECG leads increases the diagnostic sensitivity for STEMI. 3 However, additional leads required electrode repositioning and a change in patient positioning to obtain V3R-V6R and V7-V9. For this reason and others, they are not routinely done.

Pin on nurse info Ekg, Ekg placement, Ekg leads
Posterior wall myocardial infarction occurs when circulation becomes disrupted to the posterior heart. It commonly cooccurs with inferior or inferolateral MI, but when in isolation, posterior myocardial infarction represents a diagnostic challenge.
12Lead ECG Placement Guide with Illustrations
Thus, the 12-lead ECG does not display ST segment elevations during posterior (posterolateral) transmural ischemia. On the other hand, leads V1-V3 (occasionally V4) may detect the injury currents and present them as ST segment depressions. These depressions are reciprocal ST segment depressions, meaning that they mirror the ST segment elevations.
Five ECG Patterns You Must Know R.E.B.E.L. EM Emergency Medicine Blog
Posterior extension of an inferior or lateral infarct implies a much larger area of myocardial damage, with an increased risk of left ventricular dysfunction and death. Isolated posterior infarction is an indication for emergent coronary reperfusion.
ECG Educator Blog Posterior ECG Lead Placement
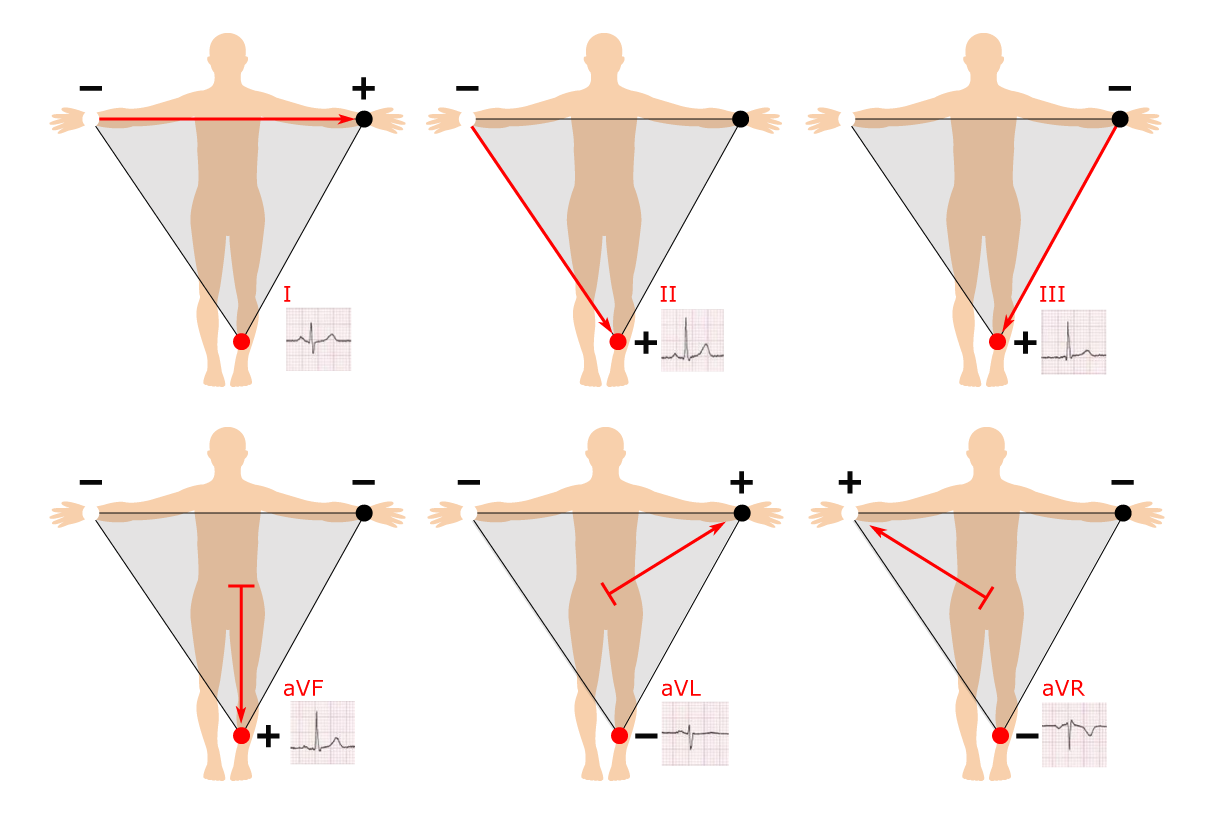
An ECG lead is a graphical description of the electrical activity of the heart and it is created by analyzing several electrodes. In other words, each ECG lead is computed by analyzing the electrical currents detected by several electrodes.
ECG Lead positioning • LITFL • ECG Library Basics
The initial 12-lead ECG ( Figure 1A) was obtained with limb leads placed on the torso position and reported as "ST elevation and possible acute inferior wall myocardial infarction (MI)". Repeat ECG with limb leads placed in standard, distal limb positions showed resolution of "ST elevation" in the inferior leads ( Figure 1B ). Figure 1A
Proper Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) Lead Placement
What are ECG criteria for posterior MI on the standard 12-lead ECG? 1 R/S wave ratio >1.0 in lead V2 Co-existing acute, inferior, and/or lateral MI Limited to leads V1 - V3: ST-segment depression (horizontal moreso than downsloping or upsloping) Prominent R wave Prominent, upright T wave

Posterior Myocardial Infarction • LITFL • ECG Library Diagnosis
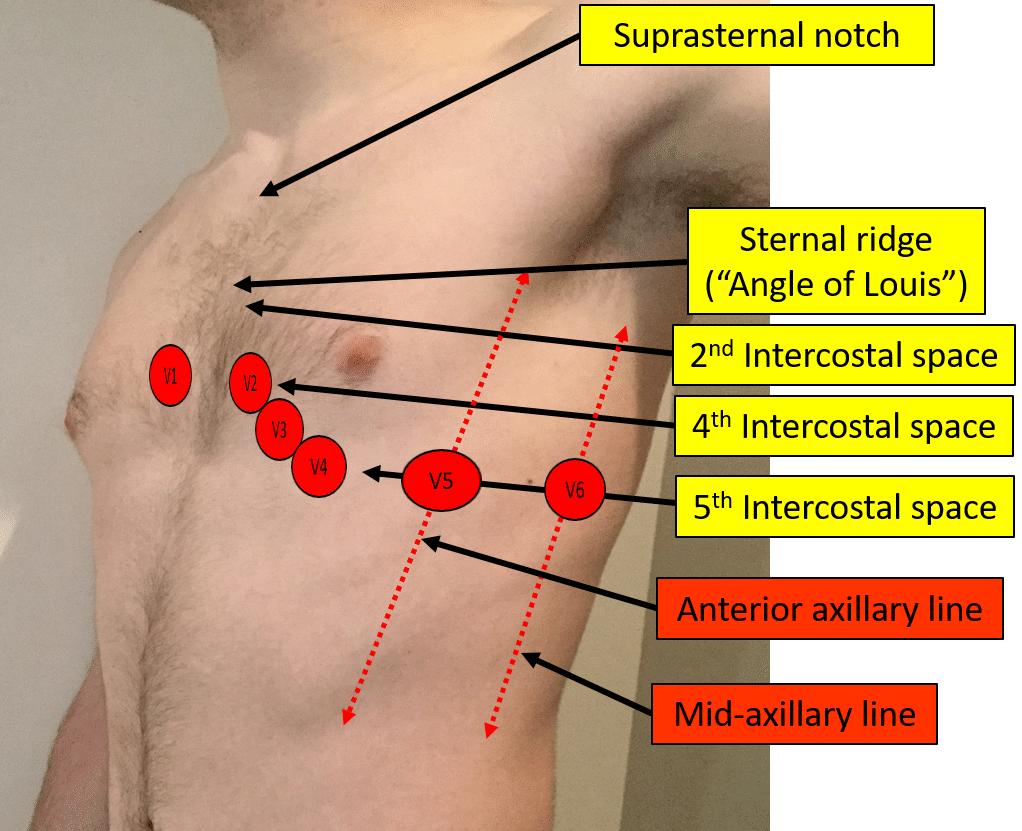
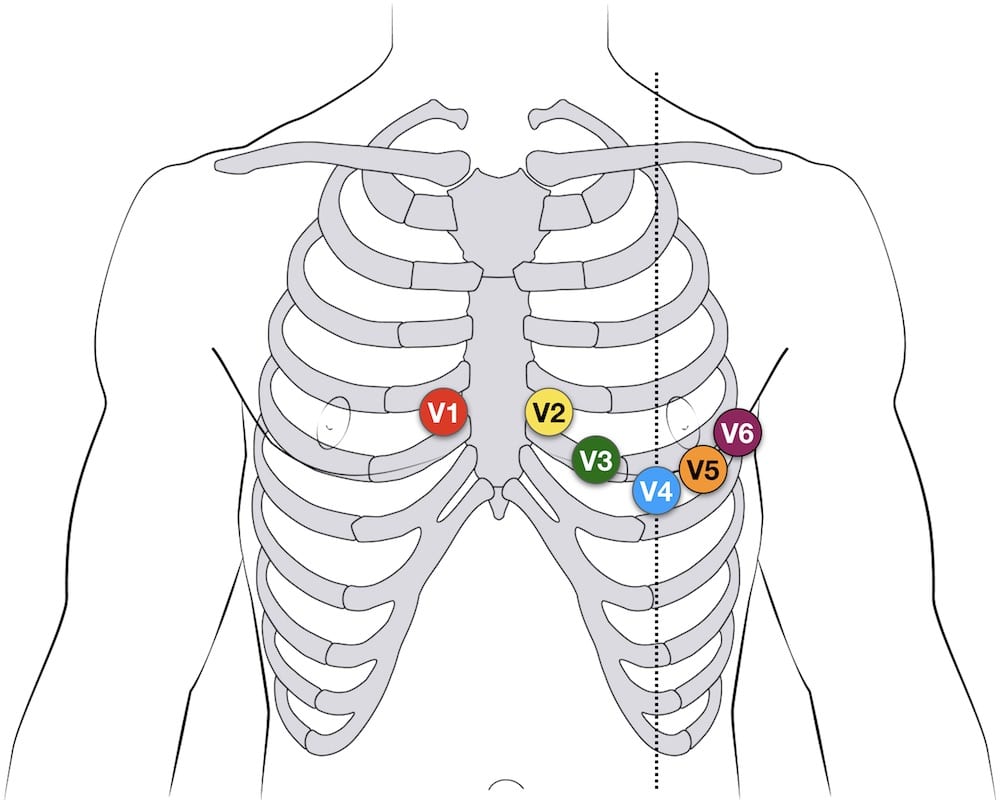
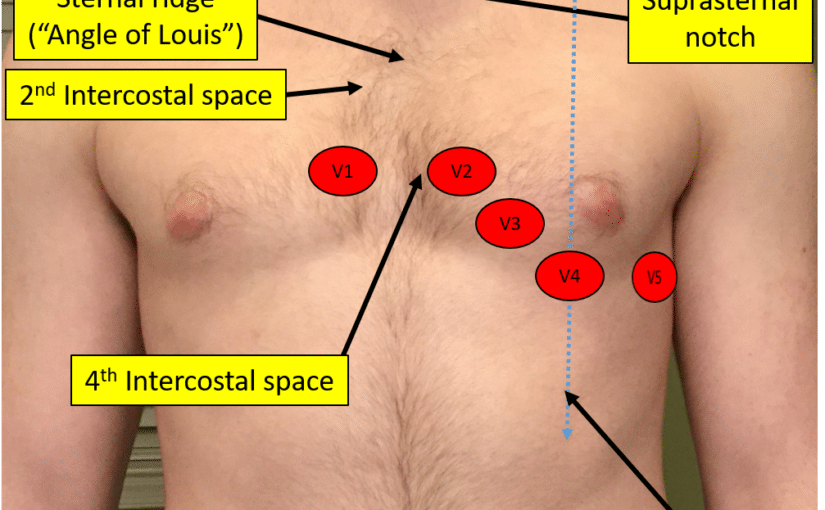
The easiest way to correctly place the electrodes is in the following order: V1 - 4th intercostal space, just to the right of the sternum. V2 - 4th intercostal space, just to the left of the sternum. V4 - On the mid clavicular line & 5th intercostal space. V6 - On the mid axillary line, horizontal with V4. V5 - Between V6 & V4.

ECG placement & misLEADing ECG’s EMbeds.co.uk
Diagnosing a posterior STEMI on 12 lead ECG can be challenging given the infarct territory being in the posterior myocardium. In this video we cover how to i.

12 Lead ECG Placement Guide Cables & Sensors
Background For decades, I noticed a significant inconsistency in the way electrocardiograms are performed. I asked nurses, EKG technicians, medical assistants, and even cardiology fellows where ECG leads/electrodes should be placed on the patient's body.

Download figure Ekg placement, Nursing information, Medical drawings
As posterior leads, when an eletrocardiogram with right-side leads has been made, to avoid confusion, you must write the word Right in the electrocardiogram header, and must write also a letter R after the name of replaced precordial leads (V3-V6). This clarify that it is a right-side electrocardiogram. previous | next If you Like it. Share it.

Posterior Ecg Lead Placement / ECG introduction at University of Texas Health Science
In uncertain cases, a posterior ECG can be obtained by placing posterior leads V7, V8, and V9 below the patients left scapula along the same horizontal plane as V6. At least 0.5mm of ST elevation in one lead indicates posterior STEMI. Posterior ECG lead placement. Case continued: The emergency provider recognized this as highly suspicious for.